4 sampling methods|random sampling in health care : manufacturer Example:A radio host asks listeners to go online and take a survey on his website. Drawback: People who voluntarily respond will likely have stronger opinions (positive or negative) than the . See more webO Eneagrama - um sistema psicológico secular - vem atraindo muito interesse e está sendo aplicado praticamente a tudo. Aclamada nacionalmente, a autora Helen Palmer condensa as idéias de seus livros populares em um guia compacto que chamará a atenção de novatos e antigos entusiastas do Eneagrama. Saiba mais
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBr/duda_rubertnsfw: comunidade sobre a influencer duda rubert. Luiza sonza, ana castela, Larissa Manoela, Gabriela saraivah, mel maia, pri caliari, duda Rubert, gabi Moura, malu camargo, melody, sofia Espanha, kauana hofemā, juh mazzoco Chama dm🔥🔥🥵
Example:A researcher stands in front of a library during the day and polls people that happen to walk by. Drawback: Location and time of day will affect the results. More than likely, the sample will suffer from undercoverage biassince certain people (e.g. those who work during the day) will not be represented as much . See moreExample:A radio host asks listeners to go online and take a survey on his website. Drawback: People who voluntarily respond will likely have stronger opinions (positive or negative) than the . See moreExample:Researchers are conducting a study of individuals with rare diseases, but it’s difficult to find individuals who actually have the disease. . See moreExample:Researchers want to know about the opinions that individuals in a city have about a potential new rock climbing gym being placed in the city square so they purposely seek out . See more
There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. Non-probability .Simple random samples. Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Sampling methods. Sampling methods review. Samples and surveys.
Choose the sampling method: Select an appropriate sampling method based on the research question, characteristics of the population, and available resources. . Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, . There are two types of sampling methods: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. It minimises the risk of selection bias. Non-probability . There are four commonly used types of probability sampling designs: Simple random sampling. Stratified sampling. Systematic sampling. Cluster sampling. Simple .
A sample is the subset of the population that you actually measure, test, or evaluate and base your results. Sampling methods are how you obtain your sample. Before beginning your study, carefully define the . We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: . Systematic Sampling 48. A systematic sample is a subset of the population in which the first member of the sample is selected at random and all subsequent members are chosen by a fixed periodic interval. An example . Learn about the types of samples such as biased samples, convenience samples, voluntary response samples, unbiased samples, and sampling methods such as stra.
Multi-stage Sampling. This method combines two or more sampling methods, such as cluster sampling and stratified sampling, to create a more complex sample design that is appropriate for the research question and the characteristics of the population being studied. How to conduct Probability Sampling
which sampling method is best
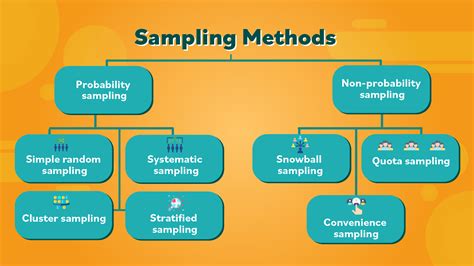
type of sampling strategy
This method ensures that different segments in a population are equally represented. To give an example, imagine a survey is conducted at a school to determine overall satisfaction. . 4. Systematic Random Sampling. Systematic random sampling is a common technique in which you sample every kth element. For example, if you were conducting . Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. What is non-probability sampling? In non-probability sampling , the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included.
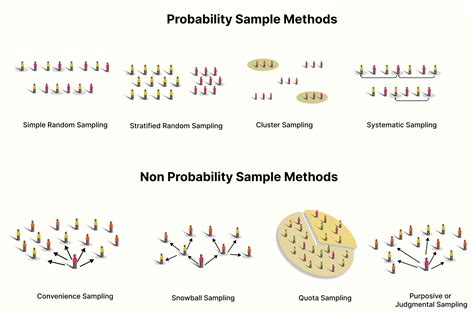
Sampling methods are the processes by which you draw a sample from a population. When performing research, you’re typically interested in the results for an entire population. Unfortunately, they are almost always too large to study fully. Consequently, researchers use samples to draw conclusions about a population—the process of making .
Sampling is a critical element of research design. Different methods can be used for sample selection to ensure that members of the study population reflect both the source and target populations, including probability and non-probability sampling. Power and sample size are used to determine the num .A visual representation of the sampling process. In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. The subset is meant to reflect the whole population and statisticians attempt to . When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the .
New sampling methods for slurry from the hose were substantially more reproducible than existing methods. For practical reasons, the mechanization of sampling is desirable, and to minimize the .4. Sampling on receipt (for acceptance) 72 4.1 Starting materials 72 4.2 Intermediates in the manufacturing process and bulk . Person responsible for performing the sampling operations. Sampling method That part of the sampling procedure dealing with the method pre-scribed for withdrawing samples. 64 Data sampling is a statistical method that involves selecting a part of a population of data to create representative samples. The fundamental aim is to draw conclusions about the entire population without having to engage with every individual data point, thus saving time, resources, and effort while still achieving accurate results.
4. Snowball sampling. This method is commonly used in social sciences when investigating hard-to-reach groups. Existing subjects are asked to nominate further subjects known to them, so the sample increases in size like a rolling snowball. For example, when carrying out a survey of risk behaviours amongst intravenous drug users, participants . In snowball sampling, the samples are added to the survey like a chain. The first group of survey subjects is chosen by the researcher, and then the subsequent set of participants is added to the . However, systematic sampling differs from simple random sampling because the systematic method doesn’t offer the same probability of being chosen for every member of a population. 4. Cluster sampling Cluster sampling involves dividing a certain population into groups, or clusters. Often, clusters correlate to different geographic areas.
Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a ‘sample’—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about .Online Researcher’s Sampling Guide, Part 4: Pros and Cons of Different Sampling Methods. Conversations about sampling methods and sampling bias often take place at 60,000 feet. That is, researchers like to talk about the theoretical implications of sampling bias and to point out the potential ways that bias can undermine a study’s conclusions. The researchers chose this sampling method due to its advantages in terms of cost and time constraints, considering the academic nature of the project and the limited timeframe available (Bhardwaj .3.4 Sampling Techniques in Quantitative Research Target Population. The target population includes the people the researcher is interested in conducting the research and generalizing the findings on. 40 For example, if certain researchers are interested in vaccine-preventable diseases in children five years and younger in Australia. The target population will be all children aged .
Non-probability sampling methods are often used in exploratory research, qualitative research, or in situations where researchers want to study a specific group or population. When to use Non-probability Sampling. Here are some situations where non-probability sampling may be appropriate:
In each case, indicate what sampling method was used: Every 4 th person in the class was selected. A sample was selected to contain 25 men and 35 women. Viewers of a new show are asked to vote on the show’s website. A website randomly selects 50 of their customers to send a satisfaction survey.Types Of Sampling Methods. Here we will learn about sampling methods, including random sampling, non-random, stratified sampling, systematic sampling and capture/recapture. There are also types of sampling methods worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck. A population is an entire group with specified characteristics. The target group/population is the desired population subgroup to be studied, and therefore want research findings to generalise to. A target group is usually too large to study in its entirety, so sampling methods are used to choose a representative sample from the target group.. A representative .Systematic sampling: The first person is selected randomly, and then a fixed interval is used to select additional individuals. For example, in a population of 1,000 people, the first selected individual is number 2 (shown in blue).; From there, every fourth person is selected, such as numbers 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, etc., until you reach your sample size of 100 individuals.
NMAM is a collection of sampling and analytical methods for workplace exposure monitoring. It includes methods for workplace air, surfaces, and blood and urine. NMAM includes chapters on method evaluation, sampling, and more. NIOSH or its partners have developed or adapted the methods included in the NMAM. NIOSH evaluates the methods according . Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration.
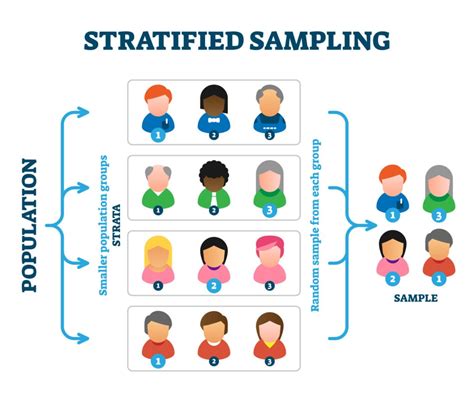
stratified sampling in health care

load cell compressive testing
WEBThe Big Bang Theory S07E05 The Workplace Proximity [1080p] WEB-DL AAC ReEnc H 26.. The Big Bang Theory S07E05 - The Workplace Proximity [720p WEB-DL H 264 DD5 1] [.. Download the big bang theory s07e05 Torrents from Our Search Results, GET the big bang theory s07e05 Torrent or Magnet via Bittorrent clients.
4 sampling methods|random sampling in health care